Parametering new residues—CDK7 as example¶
System description¶
In the previewss case, we model the CDK7-THZ1 system without take the covalent bond into consideration. In this case, we will model the covalent bond to stablize the system further.Before model with ythe covalent bond, we should take an insight into the .pdb file formate.
The CAK complex is consisited of three parts:CDK7, MAT1 and Cyclin H. In chain CDK7, Cys312 uses sulfydryl to establish a covalent bond with carbon-carbon double bond in THZ1,which displays as follows:
PDB formate¶
This part refer to the website, we just take a partion of it.
The first attribute in pdb file called"Record Type" Normally they are "ATOM","HETATM","TER" etc. "TER" indicates the end of chain of residues. "ATOM" and "HETATM" have similar formate, which display in the following picuture
The most common attribute we use when modeling are "Atom serial number", "Atom name", "Residue name", "Chain identifier", "Residue sequence number","Segment identifer", corresponding select in vmd show as follows:
Record atomid resname&resid segname
HETATM 1 CL THZCT 312 106.704 91.495 82.326 1.00 0.00 THZCCL
HETATM 2 C1 THZCT 312 108.168 92.209 81.694 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 3 C2 THZCT 312 108.288 92.495 80.315 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 4 N1 THZCT 312 109.370 93.043 79.742 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 5 C3 THZCT 312 110.412 93.299 80.584 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 6 N2 THZCT 312 111.510 93.858 80.002 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 7 C4 THZCT 312 112.795 94.205 80.519 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 8 C5 THZCT 312 113.902 94.352 79.647 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 9 C6 THZCT 312 115.172 94.714 80.143 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 10 N3 THZCT 312 116.259 94.971 79.248 1.00 0.00 THZC N
Relationship between PDB PSF RTF and PRM File¶
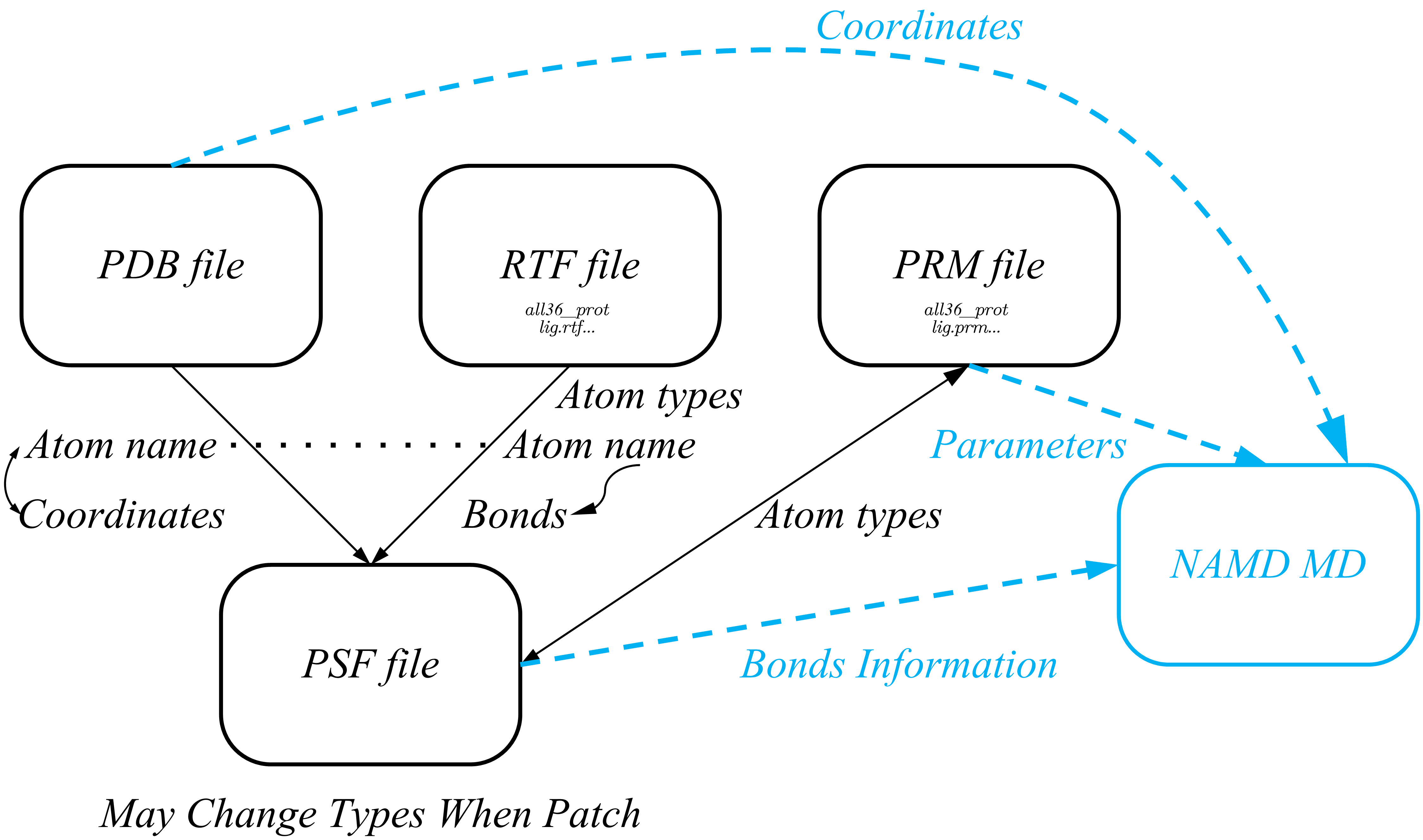
Before we start manually change these file, we should take an insight into their composition and relationship. PDB files restore coordinate information and corresponding for atom names, RTF files restore atom names, atom types, bonding information which corresponding for atom names. We use PDB file and RTF file to gengrate the PSF files we need. When running MD, we need coordinate information from pdb file, bonding information from psf file and bond's paarmeters from prm files.The detailed relationship displays in the following picture.
Build new residue's pdb¶
Solution1: Manually Modify .pdb File and then Model¶
Open THZ1's pdb file and manually paste it to CDK7'S pdb file. The covalent bond is between THZ1 and Cys312, we should save CDK7-residue 312 and THZ1 to a new pdb file named THZC. After that, we use VMD console to change new pdb file's record type,resid, resname, segname, chain name to consistent.
Soultion2: Modify the pdb file with .tcl script¶
The main task to model a covalent bond is to obtain its topology file and force fild file. To meet this task, we should first build a new pdb file which contains covalent bond linked residues and rename it as a new residue. And after, we use CHARMM-GUI and some manually patch way to model the system. To build a pdb file contains the residues linked by covalent bond, all attributes of two previous residues must be same. We can use following script to build:
package require psfgen
# Read topology file
topology top_all36_prot.rtf
topology toppar_all36_prot_na_combined.str
topology par_all36_na.prm
topology par_all36m_prot.prm
topology top_all36_na.rtf
topology toppar_all36_prot_fluoro_alkanes.str
topology top_all36_cgenff.rtf
topology thz1.rtf
#rename the residues
pdbalias residue HIS HSE
pdbalias atom ILE CD1 CD
# Build protein segment
segment THZ1 {
pdb ligandrm.pdb
}
segment CDK7 {
pdb CDK7.pdb
first ACE
last CT3
# mutate 164 SEP
}
patch THPB CDK7:170
patch SP2 CDK7:164
segment MAT1 {
pdb MAT1.pdb
first ACE
last CT3
}
segment CycH {
pdb CycH.pdb
first ACE
last CT3
}
coordpdb ligandrm.pdb THZ1
coordpdb CDK7.pdb CDK7
coordpdb MAT1.pdb MAT1
coordpdb CycH.pdb CycH
guesscoord
writepdb complex.pdb
mol delete all
mol load pdb complex.pdb
set sel2 [atomselect top "resid 312 and segname CDK7"]
set sel1 [atomselect top "segname THZ1"]
set all [atomselect top "all"]
$sel2 set resname THZC
$sel1 set resname THZC
$sel1 set segname THZC
$sel2 set segname THZC
set sel3 [atomselect top "segname THZC and noh"]
set sel4 [atomselect top "resid 1"]
$sel4 set resid 312
$sel4 set chain T
$sel3 writepdb model/THZC.pdb
sed -i "s/ATOM /HETATM/g" model/THZC.pdb
sed -i "s/THZCJ/THZCT/g" model/THZC.pdb
exit
set sel3 [atomselect top "segname THZC and noh"] are add to delete hydrogen when build up the new residue.
+ We should change resid, resname, chain and segname consistent.
+ Atom Type also should be changed to consisitent, and be the"HETATM" type in order to meet CHARMM-GUI "Ligand Reader & Modeler"'s input need, command sed -i "s/ATOM /HETATM/g" model/THZC.pdb is add to meet this requirement.
+ Since we have applied patchfirst ACE last CT3 to CDK7 segment, when we build the new system, if one of the residues is located in N-terminal or C-terminal accidently. We should delete the patch manually,for example in CDK7 system, the preprocessing result as follows:
CRYST1 0.000 0.000 0.000 90.00 90.00 90.00 P 1 1
HETATM 1 CL THZCT 312 106.704 91.495 82.326 1.00 0.00 THZCCL
HETATM 2 C1 THZCT 312 108.168 92.209 81.694 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 3 C2 THZCT 312 108.288 92.495 80.315 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 4 N1 THZCT 312 109.370 93.043 79.742 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 5 C3 THZCT 312 110.412 93.299 80.584 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 6 N2 THZCT 312 111.510 93.858 80.002 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 7 C4 THZCT 312 112.795 94.205 80.519 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 8 C5 THZCT 312 113.902 94.352 79.647 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 9 C6 THZCT 312 115.172 94.714 80.143 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 10 N3 THZCT 312 116.259 94.971 79.248 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 11 C7 THZCT 312 117.047 96.079 79.334 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 12 C8 THZCT 312 118.237 96.253 78.438 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 13 C9 THZCT 312 119.385 96.879 78.969 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 14 C10 THZCT 312 120.484 97.173 78.151 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 15 C11 THZCT 312 120.447 96.890 76.781 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 16 N4 THZCT 312 121.535 97.233 75.927 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 17 C12 THZCT 312 121.960 98.507 75.761 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 18 C13 THZCT 312 123.120 98.793 74.841 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 19 C14 THZCT 312 124.503 98.735 75.552 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 20 C15 THZCT 312 124.937 97.277 75.818 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 21 N5 THZCT 312 126.208 96.830 75.101 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 22 C16 THZCT 312 127.418 97.150 75.937 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 23 C17 THZCT 312 126.355 97.363 73.694 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 24 O1 THZCT 312 121.424 99.445 76.331 1.00 0.00 THZC O
HETATM 25 C18 THZCT 312 119.315 96.262 76.244 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 26 C19 THZCT 312 118.210 95.951 77.061 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 27 O2 THZCT 312 116.825 96.970 80.149 1.00 0.00 THZC O
HETATM 28 C20 THZCT 312 115.356 94.827 81.529 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 29 C21 THZCT 312 114.280 94.702 82.402 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 30 C22 THZCT 312 113.011 94.442 81.890 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 31 N6 THZCT 312 110.386 93.024 81.913 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 32 C23 THZCT 312 109.306 92.511 82.488 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 33 C24 THZCT 312 109.421 92.330 83.943 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 34 C25 THZCT 312 108.410 92.300 84.890 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 35 N7 THZCT 312 108.936 92.100 86.152 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 36 C26 THZCT 312 110.288 92.011 86.102 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 37 C27 THZCT 312 111.248 91.815 87.082 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 38 C28 THZCT 312 112.599 91.768 86.719 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 39 C29 THZCT 312 112.965 91.907 85.379 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 40 C30 THZCT 312 111.982 92.085 84.400 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 41 C31 THZCT 312 110.628 92.151 84.750 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 42 N THZCT 312 122.794 100.818 77.632 1.00 0.00 THZC N
HETATM 43 CA THZCT 312 123.614 99.968 78.494 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 44 CB THZCT 312 125.081 100.048 78.070 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 45 SG THZCT 312 125.332 100.043 76.278 1.00 0.00 THZC S
HETATM 46 C THZCT 312 123.480 100.321 79.970 1.00 0.00 THZC C
HETATM 47 O THZCT 312 124.423 100.156 80.743 1.00 0.00 THZC O
HETATM 48 NT THZCT 312 122.617 100.691 80.314 0.00 0.00 THZC
HETATM 49 CAT THZCT 312 123.973 99.940 81.474 0.00 0.00 THZC
END
HETATM 48 NT THZCT 312 122.617 100.691 80.314 0.00 0.00 THZC
HETATM 49 CAT THZCT 312 123.973 99.940 81.474 0.00 0.00 THZC
Generate new residue's Force Fild Files¶
After we have obtained the new residue's pdb file.We can use CHARMM-GUI to obtain new residue's FF files like before. First we upload THCC.pdb to CHARMM-GUI ligand reader. But as we don't provide bonding information, we may get the wrong configeration like below.
So, we need to revise the configeration to the correct one and generate the .prm file and .prm file. (SMILES of THZ1:"CN(C)C/C=C/C(=O)NC1=CC=C(C(=O)NC2=CC=CC(NC3=NC=C(Cl)C(C4=CNC5=CC=CC=C54)=N3)=C2)C=C1")
Model the whole system¶
package require psfgen
# Read topology file
topology top_all36_prot.rtf
topology toppar_all36_prot_na_combined.str
topology par_all36_na.prm
topology par_all36m_prot.prm
topology top_all36_na.rtf
topology toppar_all36_prot_fluoro_alkanes.str
topology top_all36_cgenff.rtf
topology lig.rtf
#rename the residues
pdbalias residue HIS HSE
pdbalias atom ILE CD1 CD
segment CDK7 {
pdb CDK7_complete.pdb
first ACE
last CT2
}
patch THPB CDK7:173
patch SP2 CDK7:167
segment MAT1 {
pdb MAT1.pdb
first ACE
last CT2
}
segment CycH {
pdb CycH.pdb
first ACE
last CT2
}
coordpdb CDK7_complete.pdb CDK7
coordpdb MAT1.pdb MAT1
coordpdb CycH.pdb CycH
guesscoord
writepdb CDK7-THZC.pdb
writepsf CDK7-THZC.psf
mol delete all
package require solvate
package require autoionize
mol load psf CDK7-THZC.psf pdb CDK7-THZC.pdb
solvate CDK7-THZC.psf CDK7-THZC.pdb -t 12 -o solvated_CDK7-THZC
mol delete all
autoionize -psf solvated_CDK7-THZC.psf -pdb solvated_CDK7-THZC.pdb -sc 0.15 -o system
file delete solvated-CDK7-THZC.pdb
file delete solvated-CDK7-THZC.psf
file delete CDK7-THZC.pdb
file delete CDK7-THZC.psf
mv system.pdb ../common3
mv system.psf ../common3
cd ../common3
vmd -dispdev text -e measure.tcl -args system
vmd -dispdev text -e fix_backbone_restrain_ca_with_ligand.tcl
#vmd -dispdev text -e cov_system_build.tcl
exit
Modify Parameters or Build Parameters with Quantum quantum chemical calculation¶
References¶
gxf's github:https://gxf1212.github.io/notes/#/techniques/Linux-fundamental